Analysis
What are required for performing analyses with high reliability are an appropriate operation environment, state-of-the-art analysis instruments and analysis engineers equipped with reliable skills.
Our analysis division has been performing analyses and evaluations which are essential for assuring product quality and developing new materials, by adopting knowledge and experiences accumulated as a manufacturer of high purity materials.
As well as additional analyses we perform for customers purchasing our products, we will accept your order for analysis only.
Main operations of the analyses are performed in an analysis-dedicated building which is equipped with temperature and humidity control and a dust removing instrument. In the analysis of infinitesimal amount of impurities, incorporation of impurities from the environment is prevented by performing processes from pre-processing to measurement in a clean room.
Clean Room and Clean Fume Hood
When analyzing high-purity products, we perform pre-processing and analysis in special environments.
※“Class 100” denotes that the number of particles of size 0.5 µm or larger permitted per cubic foot (approximately 28 L) of air is smaller than 100.

Class 100 clean fume hood

Class 1000 clean room
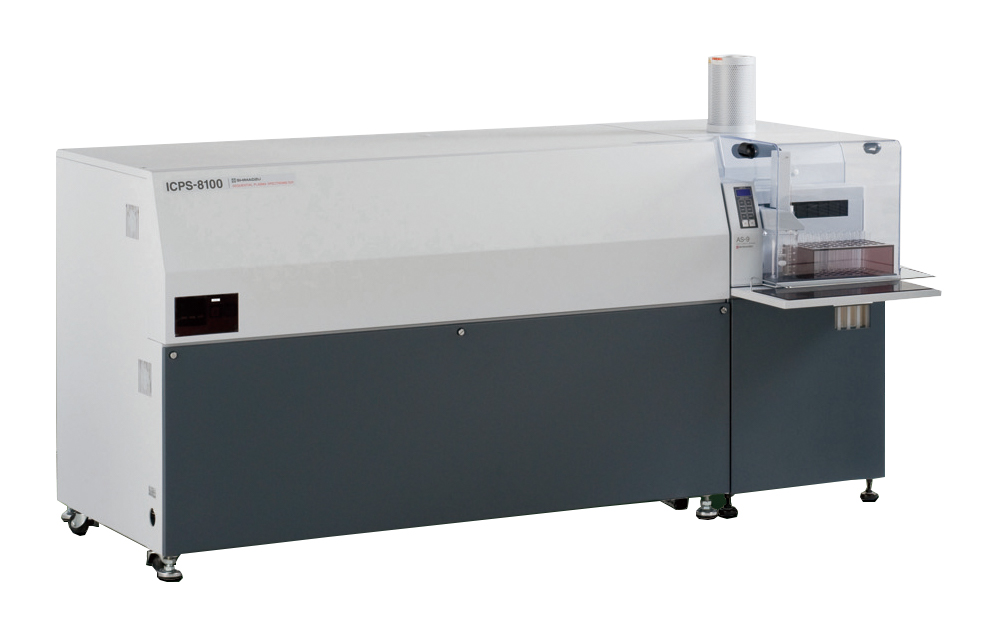
ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer)
Analysis Mechanism
ICP-MS is a high-sensitivity analysis instrument for inorganic elements, where a sample in a solution form is atomized into high temperature argon plasma and elements thereby ionized are mass-analyzed. Almost of elements in the periodic table can be simultaneously analyzed, and the measurement range of concentration extends from ppb to ppt.

Analysis Mechanism

ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer)
Analysis Mechanism
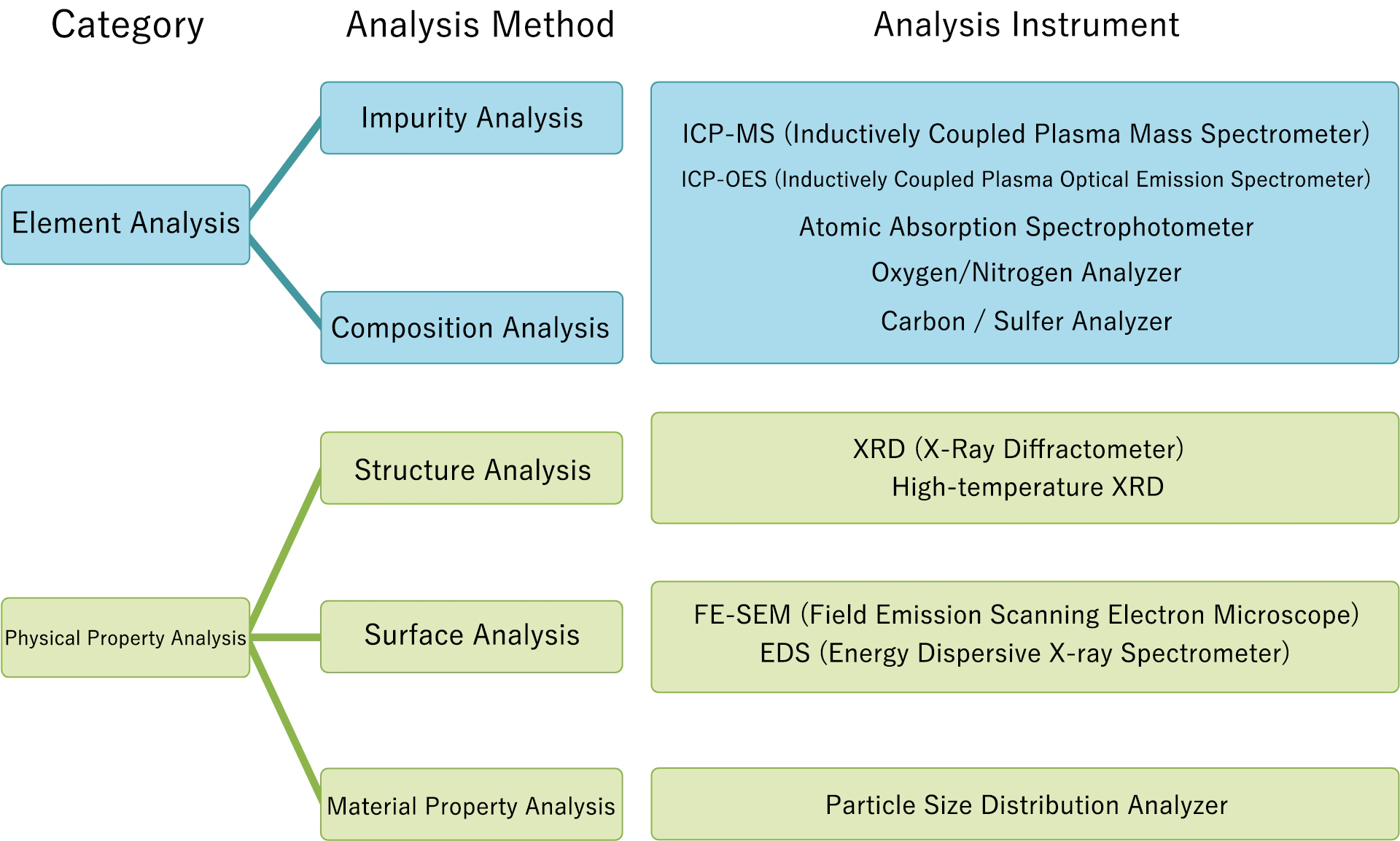
ICP-OES uses the same excitation source as that used in ICP-MS, but measures spectra of the excited light by spectrally separating the light using a spectroscope. As wavelengths of the light are specific to respective elements and intensities of the light are proportional to the quantities of respective elements, highly sensitive qualitative and quantitative analyses are possible. ICP-OES has features of having a dynamic range as wide as 4 to 5 decades and of enabling simultaneous quantitative analysis on multiple elements.
*ICP-OES is also referred to as ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometer)
Example of measured chart


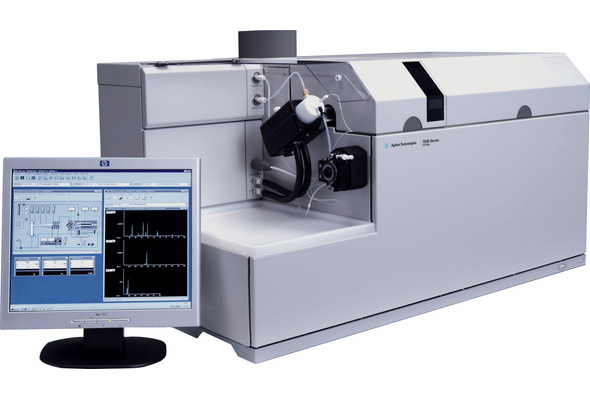
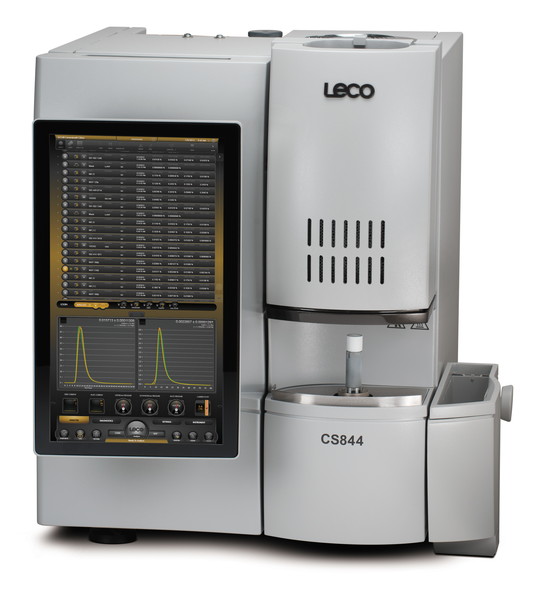
Carbon/Sulfer Analyzer
Analysis Mechanism
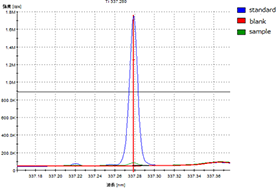
A solid sample is put into a ceramic crucible along with a combustion improver, and is caused to burn in a high concentration oxygen stream by radio frequency current. Qualitative analysis of carbon and sulfur is performed by measuring spectra of gas components contained in the sample using an infrared detector.
Example of extracted peak for Carbon

ceramic crucible for the analysis

XRD (X-ray Diffractometer)
XRD (X-ray Diffractometer)
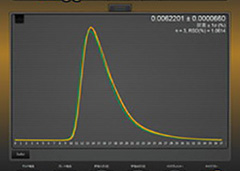
When a powder or solid sample is irradiated by X-ray beams, diffracted X-ray beams from the polycrystalline substances in the sample are detected. Qualitative analysis (identification) is performed by comparing measured data with standard data in terms of positions and intensities of the diffracted X-ray beams.
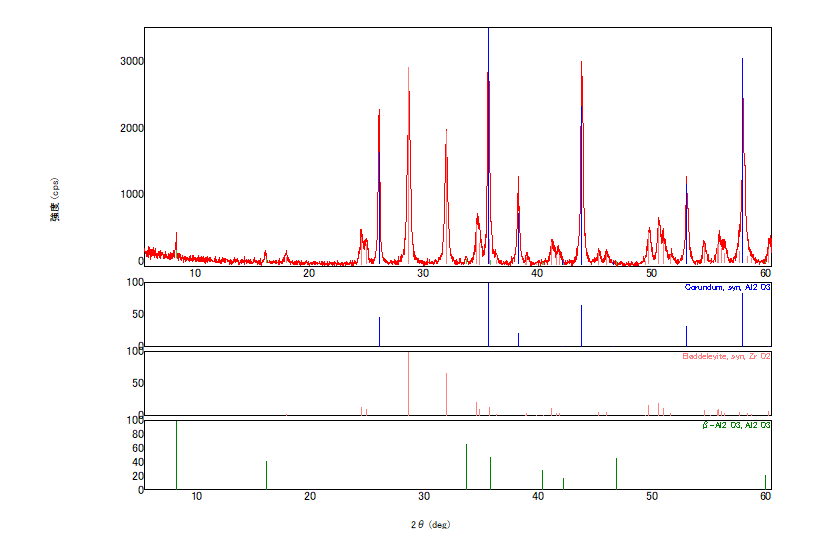
XRD (X-ray Diffractometer) chart
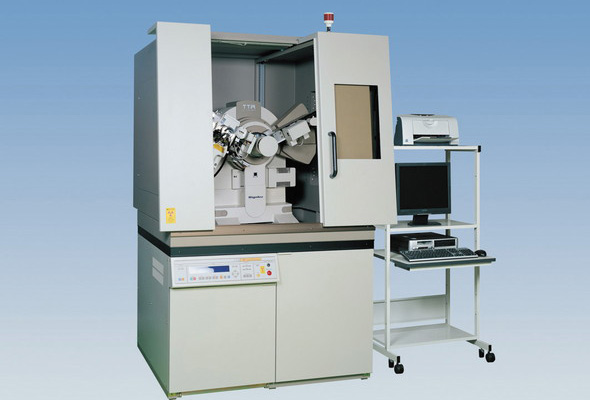

High-temperature XRD
Analysis Mechanism
This high-temperature unit is used in combination with the above-described XRD system. By heating up a sample to high temperatures, information on change with increasing temperature in the sample’s crystal structure and physical state (phase diagram) is attained. Analysis in an inert gas atmosphere or in vacuum is also possible.

High-temperature XRD
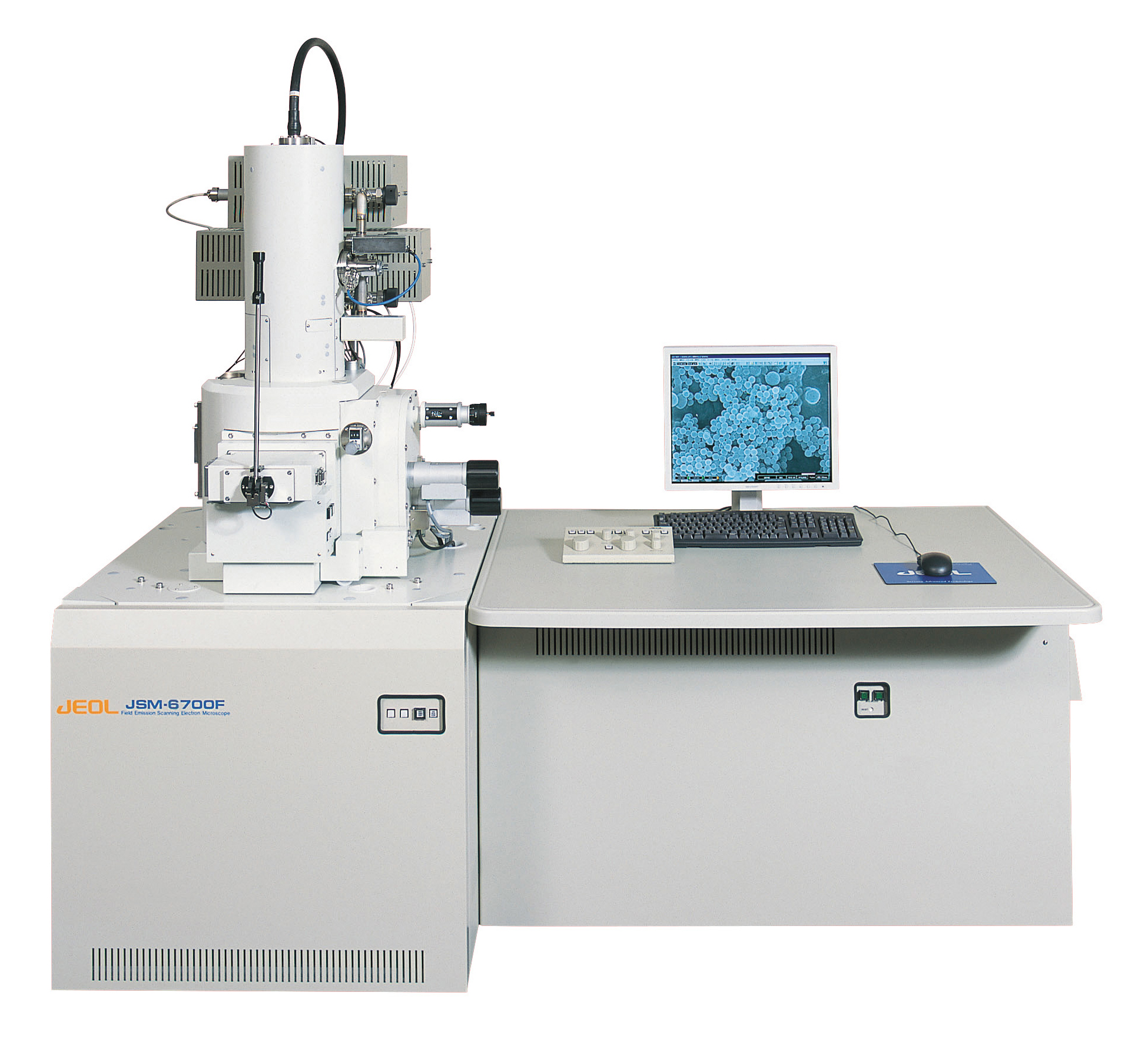
FE-SEM (Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope)
Analysis Mechanism
Irradiating a sample with narrow incident electron beams, an image of secondary electron beams emitted from the sample is obtained and, thereby, surface irregularity, shape and size of the sample is observed.
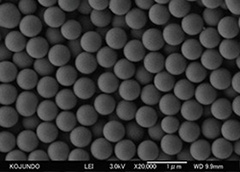
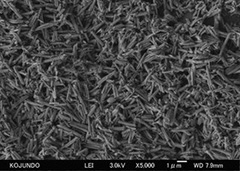
example of SEM observation of powders

EDS (Energy Dispersive
X-ray Spectrometer)
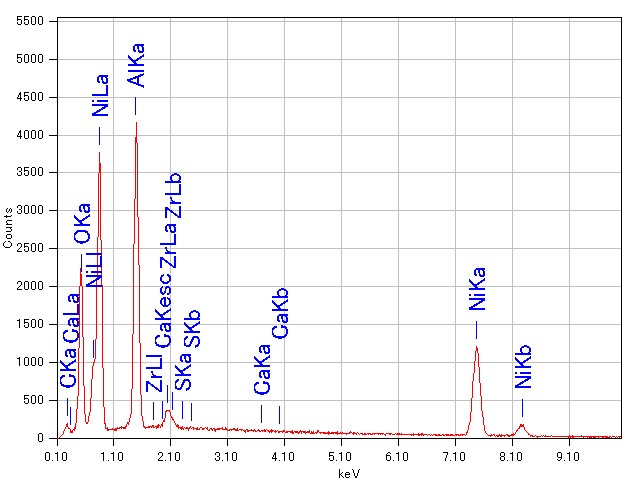
Analysis Mechanism
When a sample is irradiated with narrow incident electron beams, various electrons and electromagnetic waves are emitted from the sample. Using energies of characteristic X-rays thus emitted, element analysis and mapping analysis can be performed.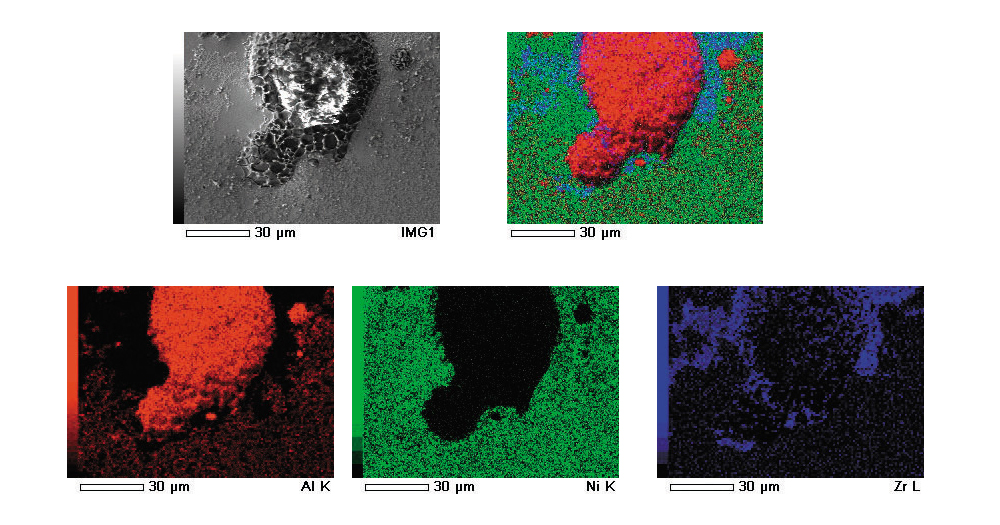
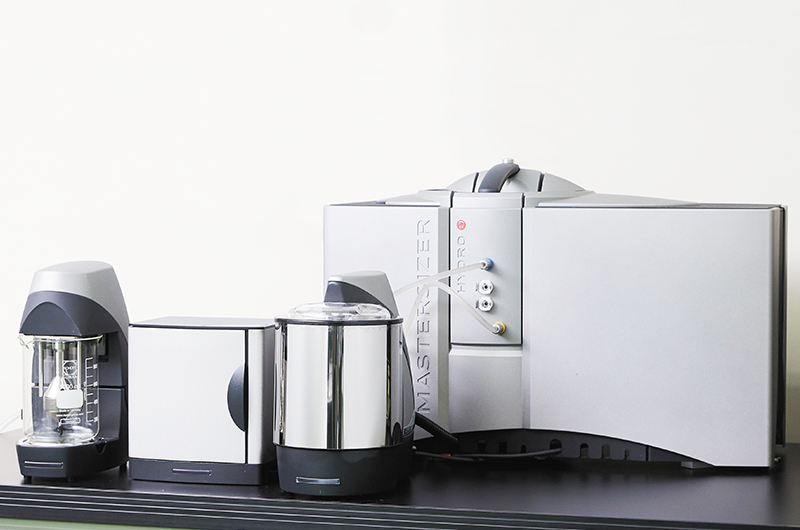
Particle Size Distribution Analyzer
Analysis Mechanism
When a sample of powders dispersed in a solution is irradiated with laser light, there occurs a diffraction/scattering phenomenon. As distribution of light intensity of the phenomenon is dependent on the particle size, the particle size can be measured from the phenomenon. Calculation based on the diffraction/scattering theory is performed on the assumption that the particles are completely spherical in shape.

