- 高純度化学研究所
- ENGLISH
- Product Guide
- Contract Services
- Contract Sintering
Contract Sintering
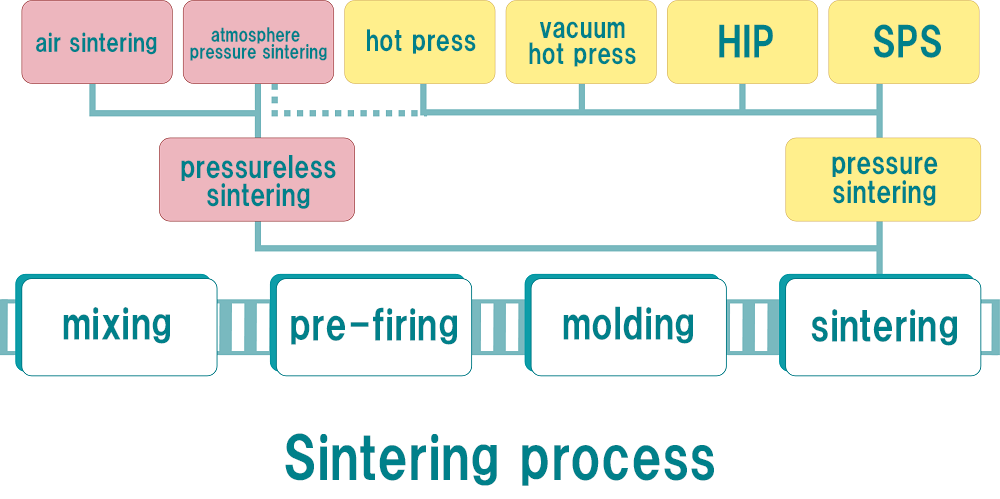
Sintering Methods
Sintering is a technology for producing a dense object by heat-compacting powders such as of a metal and an oxide at a high temperature.
We have been fabricating ceramics by five kinds of sintering methods including air sintering, hot-pressed (HP) sintering, mold pressed (including CIP (Cold Isostatic Press) sintering, spark plasma sintering (SPS) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) sintering.
Further, as we have set up environments for synthesis and preparation of various kinds of powders, we can meet your needs of not only popular fine ceramics with high density and high quality but also special ceramics which have not been achieved yet in the world.
In order to fabricate materials in accordance with your requests, we possess a variety of sintering apparatuses.
We can deal with highly active compounds, which are difficult to treat in the air, materials difficult to fabricate by conventional sintering methods, and so on, and we will make suggestions about an optimum sintering method and products, in combination with our considerable number of technologies of material synthesis, pulverization and granulation.
Air Sintering
In the sintering process, we usually use material powders with a purity ranging from 99.9 to 99.999 %.
We have been fabricating sputtering targets and tablets of oxides by mainly air sintering.
Spray Dryer
While transforming slurry into fine grains using a nozzle (spray type) or a high-speed rotation disc (centrifugal type) within the dryer main body, thereby increasing their surface area per unit volume, the fine grains are made in contact with a hot blast successively and thereby dried instantaneously. Thereby, even for a substance sensitive to heat, hollow granulated powders having high fluidity can be obtained with their quality being changed only a little. The granulated powders are easy to crush, and accordingly a high-density molded product can be obtained from the powders.
Features of the spray drier
- Dry powders can be obtained in a short time.
- Obtained dry powders have a spherical shape having high fluidity.
- Dry powders having sharp particle size distribution can be obtained.
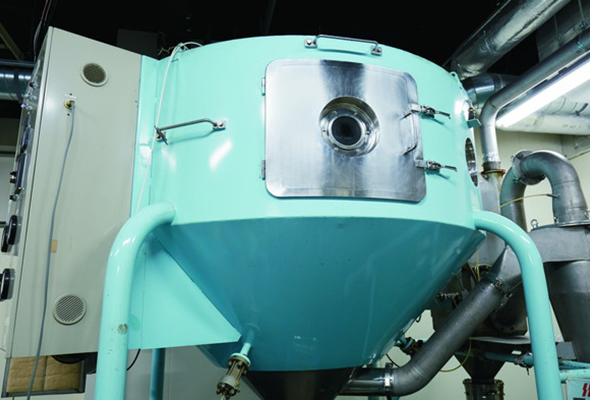

10000 kN Powder Molding Machine
Powders are packed into a desired mold and molded in one axial direction.
A3cylinder method is adopted to enable pressure control in a wide range from 100 to 10000 kN.
Influence of springback can be suppressed by precise oil pressure control, and molding operation can be performed with high reproducibility by program control.
Features of the molding machine
- Springback can be suppressed by precise oil pressure control
- Molding operation can be performed with high reproducibility by program control.
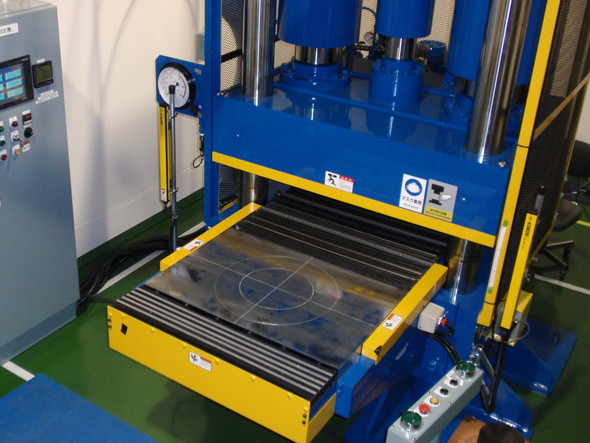

Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) Machine
Molding is performed by an isotropic hydrostatic pressure in a cylinder.
Because of the high pressure molding, molded products with very little density variation can be obtained even in a large size.
This machine is widely applicable to from small-amount production to mass production, and to from small-size products to large-size products.
- Processible size is up to about φ500 mm x 1000mm.
- Pressure of up to 200 Mpa (2040 kgf/cm2) can be applied.
Features of the CIP machine
- Because there occurs no friction with metals, differently from metallic molding, and the pressure acts isotropically, molded products with uniform density and small anisotropy.
- The pressure reduction process consists of a primary pressure reduction step by a valve and a secondary one by program control (to prevent cracking due to springback), and is enabled to be set at an optimum condition.
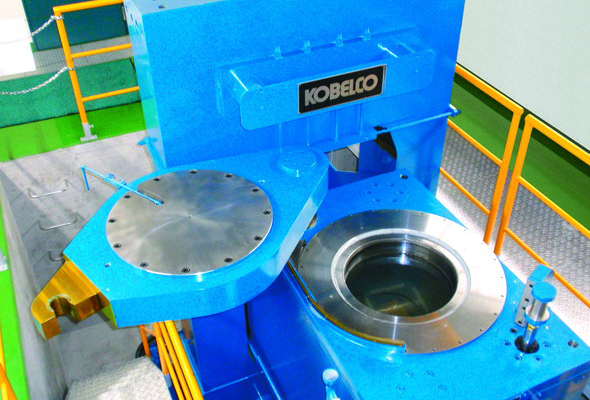

Large-size Air Sintering Furnace
This is an electric furnace for sintering in the atmosphere, where temperature can be raised up to 1700℃.
It has a maximum accommodation capacity of 500 mm square, and can be applied even to fabrication of large-size ceramic products and mass production.
Features
- An electric furnace applied mainly to synthesis and sintering of complex oxides.
- More than one samples can be sintered at the same time.
Main products
- Oxides including TiO2, ZnO, MgO, SrTiO3, LiCoO2, PZT LiF, Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 etc.
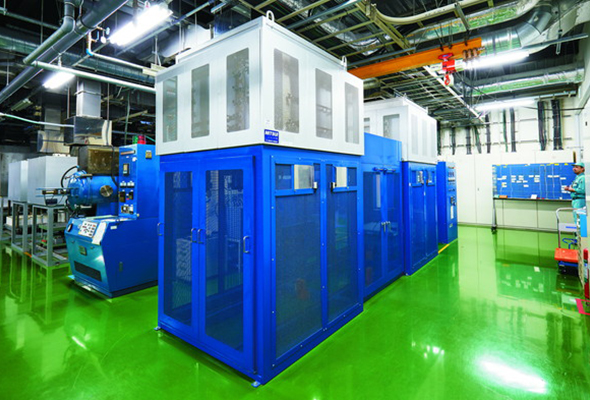

Main apparatuses for sintering process
- Hot press
- Vacuum/pressure sintering furnace
- Atmosphere sintering furnace(N2、 Ar、 H2)
Atmosphere Pressure Sintering
We use atmosphere pressure sintering for fabricating sputtering targets and tablets of various kinds of compounds including alloys and nitrides. Combining it with our melting and synthesis technologies, we can treat a variety of materials.
Vacuum Hot Press
Vacuum hot press is one of pressure sintering methods. Powders are packed in a carbon mold and then sintered with heat and pressure applied simultaneously.
Degassing is performed in an initial stage of heating, and sintering is subsequently performed in an inert gas atmosphere.
Heating up to 2000 ℃ is possible.
Processable size ranges from φ60 to φ230 mm.
Features
- Oxidation of metals can be prevented, as degassing is performed in an initial stage of heating, and sintering is subsequently performed in an inert gas atmosphere.
- High reproducibility is enabled by program control.
Main products
- Highly oxidizable metals including W-base, Mo-base, Nb-base, V-base and Ta-base ones
- Oxygen-deficient type oxides including TiOx、NbOx
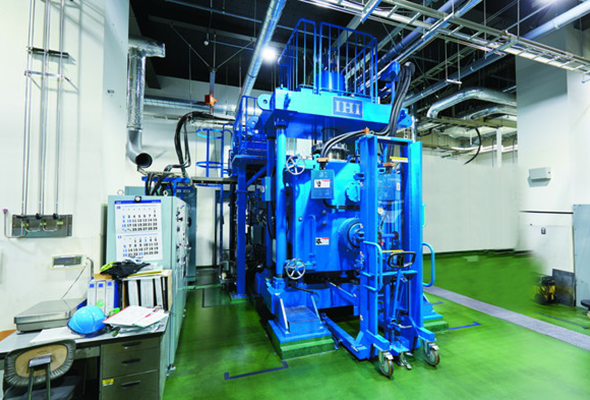

Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)


Spark plasma sintering (SPS) is one of pressure sintering methods, where pulsed electrification is employed. By using self-heating of the processing object and spark plasma energy generated between grains, both of which are caused by the pulsed electrification, rapid and dense sintering in a short time is realized.
SPS facilitates sintering of low sinterability materials (materials hard to sinter) and joining of materials hard to join.
- Sintering with no addition of binder (sintering aid) (AlN, TiN, W-Ti, Si3N4etc.)
- Sintering of complex materials and multi-component materials (oxide+metal, nitride+metal etc.)
Grain contol, grain growth suppression
- sintering of nanostructure material
- application to porous materials
Sintering example
Joined sintered body
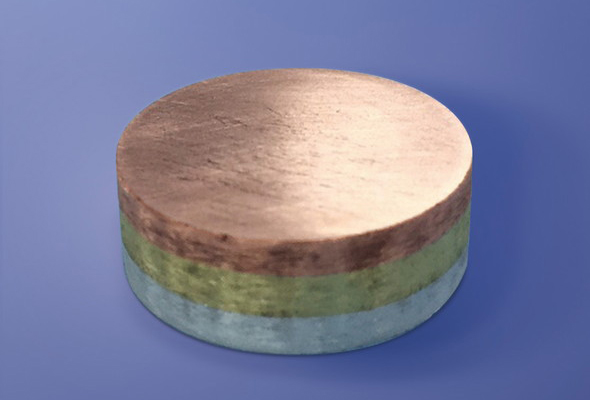
Even materials difficult to densify by sintering and/or those likely to decompose at high temperature can be sintered by SPS without destroying the structure.
Low sinterability material/High decomposability substance
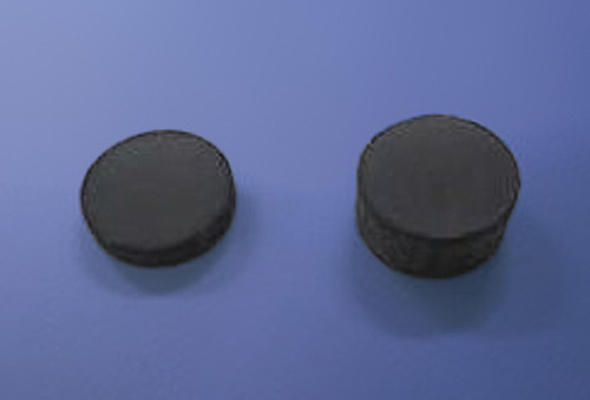

SPS enables providing a temperature gradient within a powder compact and, accordingly, sintering of gradient materials and so on also has been intensively performed.
Related apparatuses
- Hot press
- Vacuum/pressure sintering furnace
- Atmosphere sintering furnace (N2, Ar, H2)
- HIP
