CSD
What's CSD?
“CSD materials” denotes materials used for a thin film preparation method referred to as CSD (Chemical Solution Deposition), with which thin films are prepared by coating on a substrate, and the coated solution of an organic acid and the metalorganic salts are subsequently dried and then fired to form the composite metal oxide layer. (fire=heat dried chemicals to decompose farther those chemicals to form metal oxide film)
CSD materials
CSD materials are liquid materials which enable easy fabrication of compound oxide thin films, which are accomplished by coating them on a substrate by using a dip-coating or spin-coating method and then subsequently drying and firing to form the coated oxide layer. )
CSD materials are very useful as materials for research-use to perform preliminary evaluation of characteristics of functional ceramic thin films and explore their possibility. The biggest advantage of CSD materials in mass production is low cost, as well as for the materials, for a production system or facility used for the thin film process.
Our lineup of CSD materials is the one almost entirely covering the periodic table, and has been appreciated by researchers of a number of different areas.

Method of formation
Dip-coating method
In this method, a substrate is immersed in a solution of a coating material and is then pulled up slowly, thereby forming a liquid layer on the substrate.

Spin-coating method
In this method, a solution of a coating material is dripped onto a substrate in rotation and, by the effect of centrifugal force, a uniform layer is thereby formed on the substrate.
Types of CSD Materials
Types of CSD Materials
MOD coating materials are prepared, with their wettability with substrates being given the highest importance, such that they can be easily coated onto various kinds of wafers, SiO2 or glass substrates and others, using the spin coating or dip coating method or the like.
Sol-Gel type coating materials
Sol-gel materials are the ones prepared by hydrolyzing and polymerizing metalorganic compounds such as alkoxides and then dispersing thus formed colloids in a solution. As thus prepared solution contains almost no polymeric components such as organic acids, and the main component itself in the solution has been formed to be equivalent to a precursor for a ceramic material, it is generally advantageous in reducing the temperature of thin film formation.
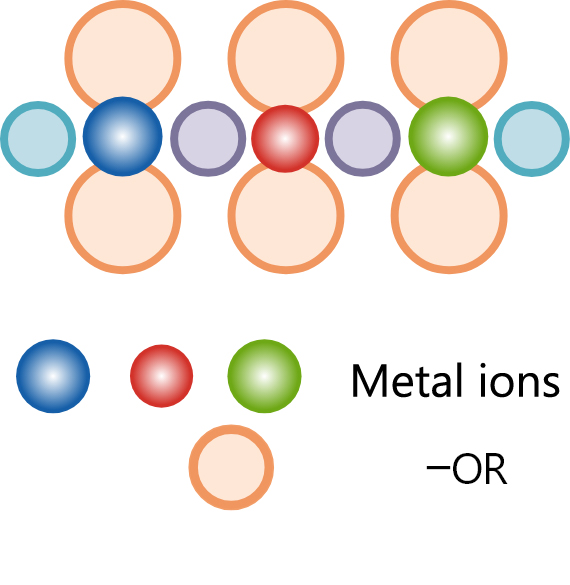

We have been having abundant experiences in producing CSD materials for various simple or complex metal oxides, as well as complex oxides, with a small quantity of doping element, and so on, to meet a wide range of needs including various customized products in accordance with applications and products for collaborative R&D, for resultant development and for the mass production.
Examples of CSD materials
Coating materials for PZT thin film formation
※You can scroll and see
| product name | PZT-20 (110/52/48), etc. |
|---|---|
| field | energy, micro-machines, semiconductor memories |
| application | thin film piezo-MEMS, high-k dielectrics/ferroelectrics |
| feature | thin film piezo-MEMS, high-k dielectrics/ferroelectrics |

Representative CSD materials of PZT family
※You can scroll and see
| product name | PZT’s after sintered | concentration |
|---|---|---|
| PZT-20 | Pb(ZrTi)O3 | 20wt% |
| PLZT-20 | (PbLa)(ZrTi)O3 | 20wt% |
| PNZT-20 | Pb(NbZrTi)O3 | 20wt% |
| PT-25 | PbTiO3 | 25wt% |
Coating materials for Magnetic garnets
※You can scroll and see
| product name | Bi-YIG, etc. |
|---|---|
| field | magneto-optics, magnetic domain observation device |
| application | magnetic sensors, magnetic imaging |
| feature | many collaborative R&D activities with universities |
One application is a magnetic transfer film for magnetic field distribution measurement, which is a technology anticipated in the area of non-destructive tests.
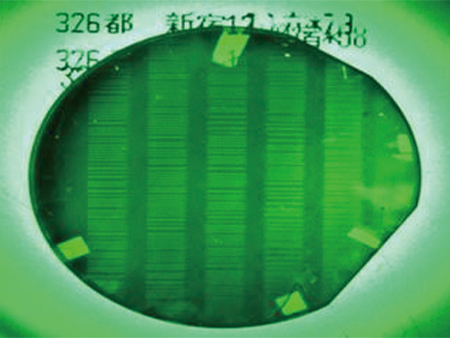
A record mark on a magnetic card visualized using a Garnet thin film.
Sol-gel type coating materials
※You can scroll and see
| product name | Si-05S, Ti-05-P, etc. |
|---|---|
| field | semiconductors, solar cells, LCD panels, sheet glass processing, etc. |
| application | glass coating materials, protection layers, passivation, etc. |
| feature | many collaborative R&D activities with universities. |