CVD
What's CVD?
CVD materials are source materials (precursors) for thin film growth of a desired material by vaporizimg a source material(s) having an appropriate vapor pressure and using chemical change in the vapor phase under various conditions.
Materials for interlayer dielectrics fabrication
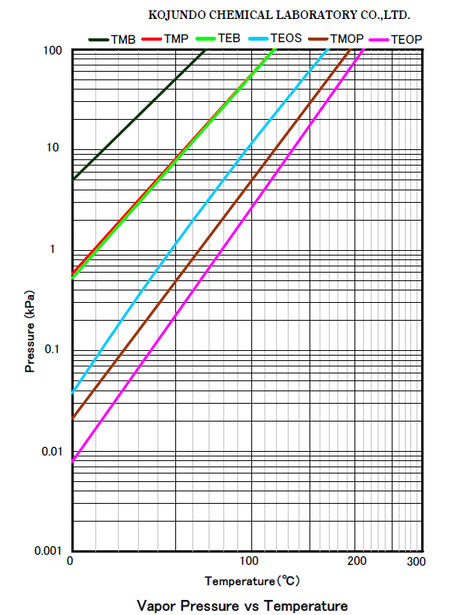
Among liquid CVD materials for silicon semiconductors, metalorganic compounds generally used currently are TEOS, TMB, TEB, TMP, TMOP and TEOP.
KOJUNDO is a pioneer in production and provision of TEOS, which is a CVD material currently used in the largest quantity for semiconductor devices, and have been producing also other various kinds of CVD materials including TEOP and TEB and the like, which are used as frequently with TEOS.
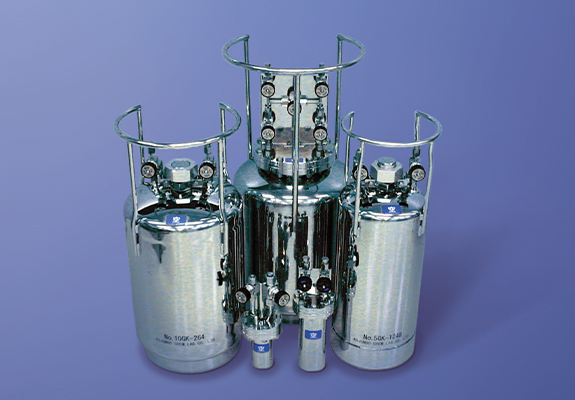

CVD materials are generally supplied in cylinders.
We can provide design and fabrication of a cylinder in accordance with the quantity to be used and specifications of the CVD system.
| abbreviated name | chemical formula |
|---|---|
| TMB | B(OCH3)3 |
| TMP | P(OCH3)3 |
| TEB | B(OC2H5)3 |
| TEOS | Si(OC2H5)4 |
| TMOP® | PO(OCH3)3 |
| TEOP® | PO(OC2H5)3 |
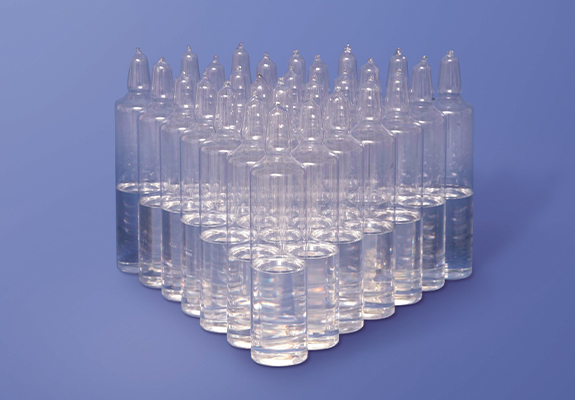

Glass ampoules are the most-used containers for supply of a small quantity of alkoxides or halides.
ALD Materials
ALD (Atomic Layer Deposition) is a method of growing a thin film by repeating growth of a single atomic layer per cycle (while not exactly), and is frequently employed for well-controlled fabrication of a thin film of a nitride or an oxide with a thickness of about 10 nm. Materials suitable for ALD are those which are highly active with an oxidant and are not likely to produce an oxide layer by self-decomposition like metal alkoxides do.
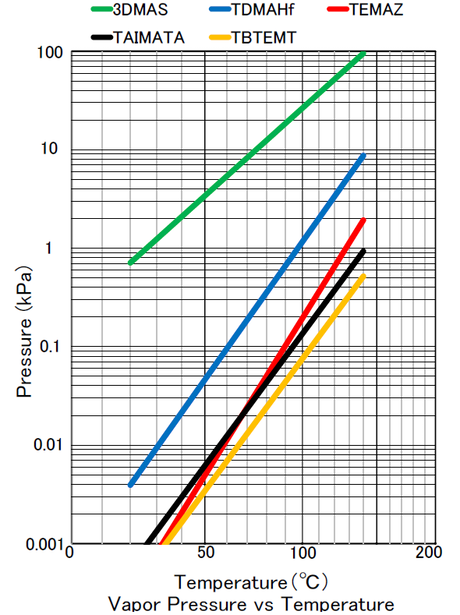
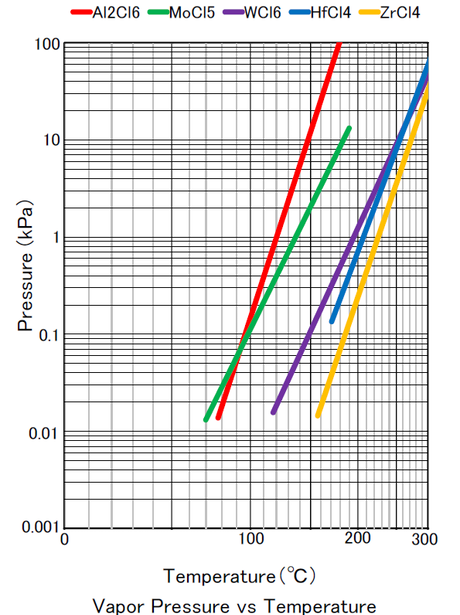
Oxides and nitrides of some metals are effective for gate dielectric and barrier layers, and metal amides, metal imides and metal chlorides are used for ALD of such metal oxides and nitrides. Metal amides, metal imides and metal chlorides are the compounds expressed as, respectively, M-NR1R2,M=NR, and MClx. Generally used ones among them are TEMAZ,TDMAH,TBTEMT,ZrCl4,HfCl4,WCl6 and AlCl3.
Properties of major amide compounds for ALD
| abbreviated name | chemical formula |
|---|---|
| 3DMAS | SiH[N(CH3)2]3 |
| TDMAH | Hf[N(CH3)2]4 |
| TEMAZ | Zr[N(C2H5)CH3]4 |
| Taimata® | Ta(N-t-C5H11)[N(CH3)2]3 |
| TBTEMT | Ta(N-t-C4H9)[N(C2H5)CH3]3 |
Properties of major halide compounds for ALD
| chemical formula |
|---|
| AlCl3 |
| MoCl5 |
| WCl6 |
| HfCl4 |
| ZrCl4 |
What are introduced here are MOCVD source materials (precursors) for high dielectric constant (high-k) and ferroelectric materials which are used in semiconductor memories including DRAMs and nonvolatile FRAMs. Generally used precursors are β-diketonates such as dpm complexes for ferroelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3(PZT), and Ta(OC2H5)5 for high-k Ta2O5.




Properties of CVD precursors for high-k/ferroelectric materials and electrodes
※You can scroll and see
| molecular weight | melting point | vapor pressure | vapor pressure | note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta(OC2H5)5 PET CAS 6074-84-6 |
406.25 | 21℃ | log10P=12.645-4505/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.56 | hydrolyzes by reacting with moisture in the air |
| Hf(O-t-C4H9)4 HTB CAS 2172-02-3 |
407.94 | 8℃ | log10P=11.265-3052/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.17 | hydrolyzes by reacting with moisture in the air |
| Al(O-sec-C4H9)3 CAS 2269-22-9 |
246.32 | -60℃ | log10P=13.325-4698/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) |
0.937 | hydrolyzes by reacting with moisture in the air |
| Ru(C5H4C2H5)2 CAS 32992-96-4 |
287.36 | 6℃ | log10P=11.875-3708/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.56 | relatively stable in the air |
| Pb(C11H19O2)2 CAS 21319-43-7 |
573.73 | 130℃ | sublimation log10P=20.545-7800/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) evaporation log10P=12.065-4480/ (t+273.15) (P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.52 | relatively stable in the air |
| Zr(O-i-C3H7)(C11H19O2)3 CAS 343311-16-0 |
700.11 | >210℃ | log10P=19.735-7924/ (t+273.15)(P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.0 | decomposes by reacting with oxygen and moisture in the air |
| Ti(O-i-C3H7)2 (C11H19O2)2 CAS 144665-26-9 |
532.58 | 160℃ | log10P=14.855-5435/ (t+273.15)(P:Pa、t:℃) |
1.0 | decomposes by reacting with oxygen and moisture in the air |
